162
CHAPTER 13
(2)
Missile lodged intramedullary
Such injuries have been described by many surgeons and the symptomatology of the
published cases varies. Although a missile of a small calibre lodged intramedullary may
cause only partial lesions, larger missiles, especially grenade splinters, usually cause
complete transections of the cord and at operation the two stumps of the cord are found
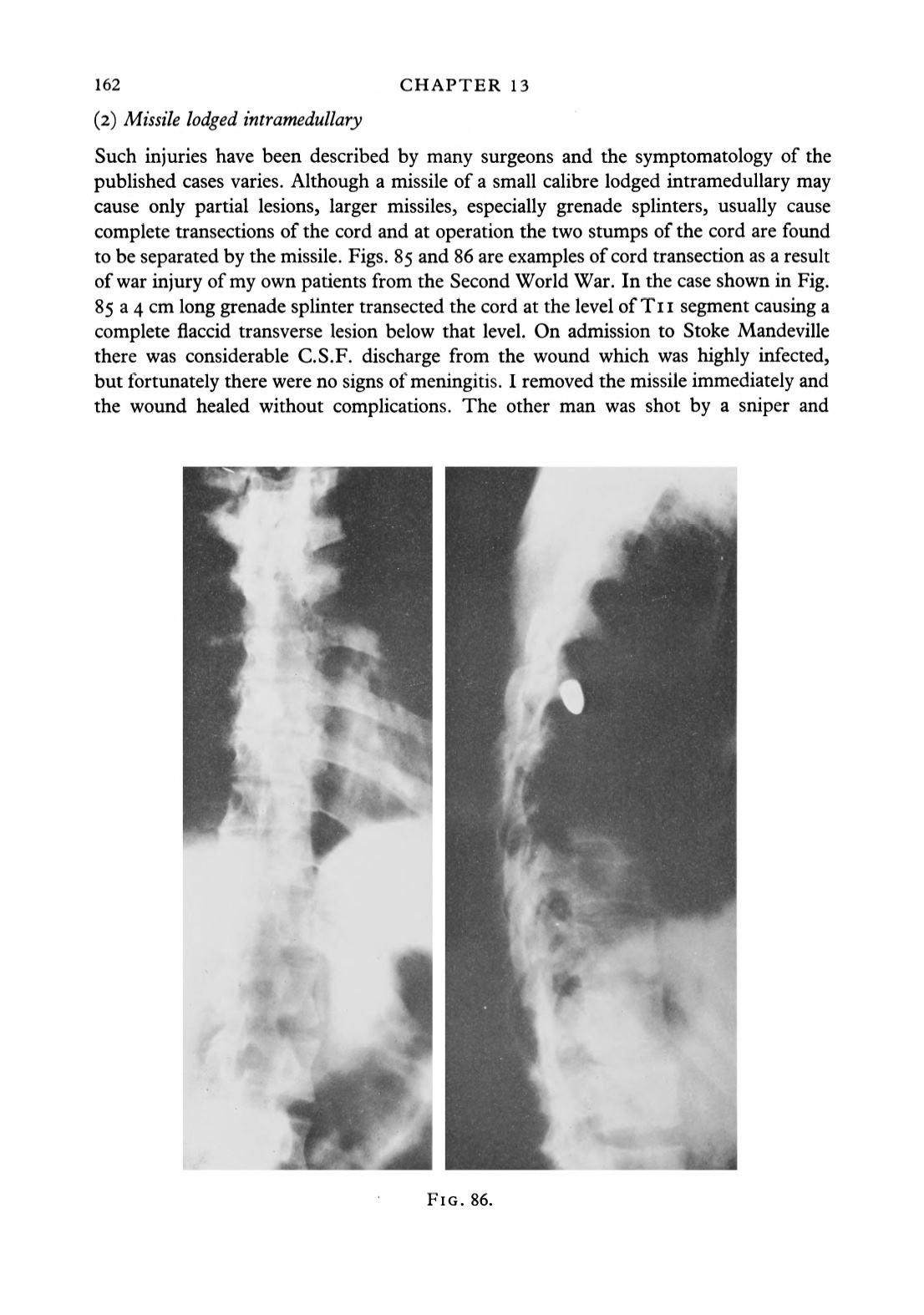
to be separated by the missile. Figs. 85 and 86 are examples of cord transection as a result
of war injury of my own patients from the Second World War. In the case shown in Fig.
85 a 4 cm long grenade splinter transected the cord at the level of Tn segment causing a
complete flaccid transverse lesion below that level. On admission to Stoke Mandeville
there was considerable C.S.F. discharge from the wound which was highly infected,
but fortunately there were no signs of meningitis. I removed the missile immediately and
the wound healed without complications. The other man was shot by a sniper and
FIG. 86.


